Internet regulation
Internet regulation covers issues such as online privacy and content, intermediary liability, net neutrality and applies to the rights and obligations of individuals and legal entities such as news media. Internet regulation is typically a national or in Europe an EU level activity:
“The EU’s Regulation on open Internet access grants end-users the directly applicable right to access and distribute the lawful content and services of their choice via their Internet access service. It enshrines the principle of open internet access: internet traffic shall be treated without discrimination, blocking, throttling or prioritisation. At the same time, the EU open internet access rules allow reasonable traffic management [..]”
Around the world however, there exist many different approaches to internet regulation, which means there are different outcomes in terms of the impact on data protection and privacy across countries and continents as the introduction of the EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) has shown.
Learn more
Regulating the Internet (School of Law, Faculty of Law at the Queensland University of Technology). This resource focuses on 4 key themes: Internet Governance and the Limits of Law; Intermediary Liability; Laws that are Explicitly Designed to Regulate Online Content or User Behaviour, and Constraining Private Power and Protecting Individual Rights on the Internet.
Internet governance
Internet governance is the development and application by governments, the private sector and civil society, in their respective roles, of shared principles, norms, rules, decision-making procedures, and programmes that shape the evolution and use of the Internet (Tunis Agenda for the Information Society, World Summit on the Information Society, 2005).

The Global Forum for Media Development has developed an excellent overview of resources on Internet Governance, actors involved and updates on the subject matter.
A useful resource to get a quick grasp of which media development principles are at stake in the different areas of Internet Governance, is the CIMA publication Media Development in the Digital Age: Five Ways to Engage in Internet Governance
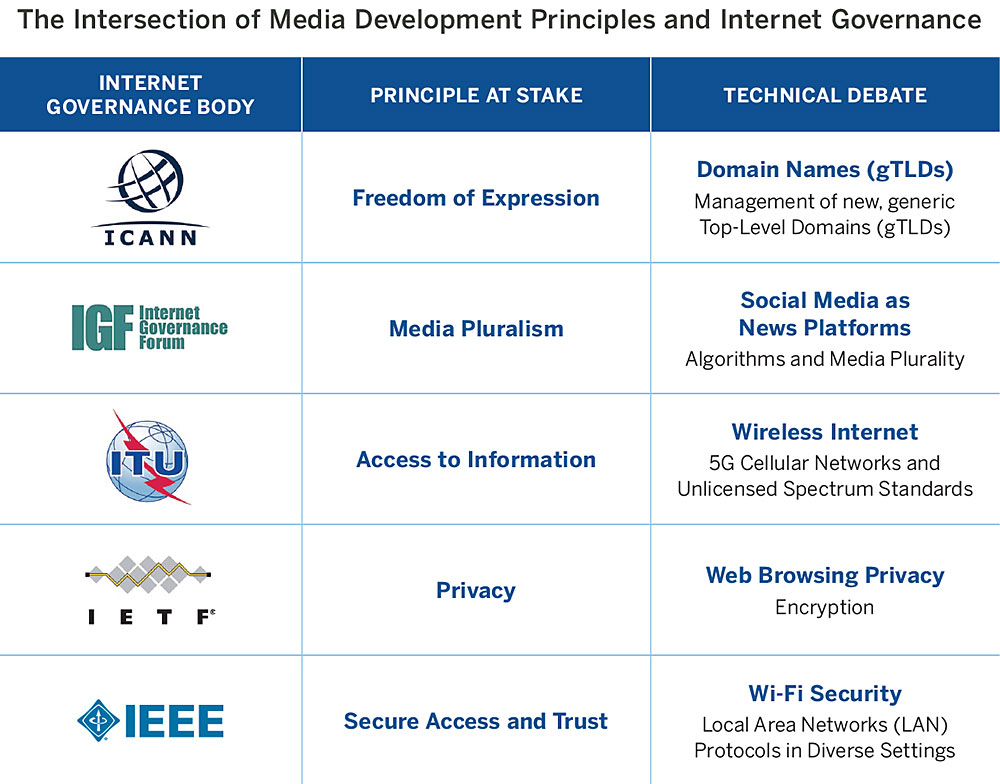
By Corinne Cath, Niels ten Oever and Daniel O’Maley, March 22, 2017
CoE standards, EU regulation
- Recommendation CM/Rec(2020)1 of the Committee of Ministers to member States on the human rights impacts of algorithmic systems
- Recommendation CM/Rec(2018)2 of the Committee of Ministers to member States on the roles and responsibilities of internet intermediaries
- Recommendation CM/Rec(2016)5 of the Committee of Ministers to member States on Internet freedom
- Recommendation CM/Rec(2016)1 of the Committee of Ministers to member States on protecting and promoting the right to freedom of expression and the right to private life with regard to network neutrality
- Recommendation CM/Rec(2015)6 of the Committee of Ministers to member States on the free, transboundary flow of information on the Internet
- EU Open Internet Policy
- EU regulation in relation to the open internet for “end-users”
